Official Name: Czech Republic (Short form name is Czechia)
National Symbol: Double-tailed Lion
Internet Domain: .cz
International Dialing Code: +420
| Location and Size | Economy | Business Climate | |
| Government | Comparative Indicators | Business Protocol | |
| Legal System | Credit and Collections | Other Sources of Info | |
| Interesting Facts | Risk Assessment |
Location and Size
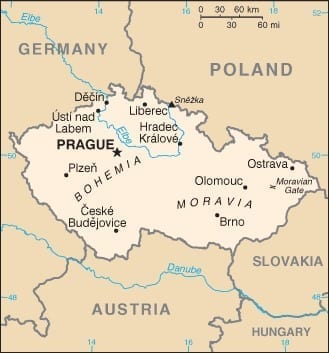
Covering an area of 78,867 sq km, the Czech Republic is slightly smaller than South Carolina. This land-locked Central European country is surrounded by Germany, Poland, Slovakia, and Austria.
Government
In January 1993, the former country of Czechoslovakia split into the Czech Republic and Slovakia.
The Czech Republic is a multi-party, parliamentary democracy made up of 13 regions. Its capital, Prague, located in the region of Bohemia, is the fourteenth largest city in Europe. The branches of government are as follows:
Executive: Chief of State: (elected by Parliament for a five-year term (eligible for a second term) President Vaclav KLAUS (since 7 March 2003); head of government: Prime Minister Petr NECAS (since 28 June 2010); cabinet: appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime minister.
Legislative: Bicameral Parliament consists of the Senate (81 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve six-year terms; one-third elected every two years); and the Chamber of Deputies (200 seats; members are elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms).
Judicial: Supreme Court (judges appointed by the president for an unlimited term); Constitutional Court (judges appointed by the president, confirmed by the Senate for a 10-year term); Supreme Administrative Court (chairman and deputy chairmen appointed by the president for a 10-year term).
Legal System
The Czech Republic has a civil law system based on former Austro-Hungarian civil codes and socialist theory. The Czech Parliament, however, has modernized many elements of the legal system.
The country has not accepted compulsory International Court of Justice (ICJ) jurisdiction. The Czech Republic does accept International Criminal Court jurisdiction.
Interesting Facts About the Czech Republic
- 90% of Czechs have completed at least secondary education.
- Czech people are the world’s heaviest consumers of beer.
- The country is renowned for its numerous spa towns, especially along the border with Germany.
- Famous Czechs include classical music composers, Bendrich Smetana and Antonin Dvorak, German-language author, Franz Kafka, and tennis champion Martina Navratilova.
- The Charles University in Prague, founded in 1348, is the oldest university in Eastern Europe
- The first sugar cubes were made in the Czech town of Dacice in 1841.
- The word “robot” is Czech. It first appeared in a drama written by Czech playwright and journalist Karel Capek called R. U. R. (Rossum’s Universal Robots).
- Prague Castle, begun in the 9th century, is listed in the Guinness Book of World Records as the largest castle in the world.
- Czech doctor Jan Jansky was the first to divide blood into four types in 1907.
Economy
The economy of the Czech Republic is one of the most developed in Central and Eastern Europe. After experiencing a sharp drop in 2009 (-4.2%) due to the global recession, the country resumed growth in 2010 , followed by another drop in 2011. As a result of the country’s heavy dependence on European demand (with exports representing 84% of GDP, 67% of which are destined for the EU) and the current difficulties plaguing its trading partners in the eurozone, the situation is expected to deteriorate further in 2012.
Long-term challenges facing the economy include dealing with a rapidly aging population, funding an unsustainable pension and health care system, and diversifying away from manufacturing and toward a more high-tech, services-based, knowledge economy.
Leading Markets (2017): Germany 32.8%, Slovakia 7.8%, Poland 6.1%, France 5.1%, UK 4.9%, Austria 4.4%, Italy 4.1%
Leading Exports – Commodities: machinery and transport equipment, raw materials and fuel, chemicals
Leading Suppliers (2017): Germany 29.8%, Poland 9.1%, China 7.4%, Slovakia 5.6%, Netherlands 5.3%, Italy 4.0%
Leading Imports – Commodities: Machinery and transport equipment, raw materials and fuels, chemicals
Top Industries: Motor vehicles, metallurgy, machinery and equipment, glass, armaments
Top Agricultural Products: Wheat, potatoes, sugar beets, hops, fruit; pigs, poultry
Comparative Economic Indicators ” 2018
| Czech Republic | Austria | Germany | Hungary | Poland | Slovakia | |
| Population (millions) | 10.6 | 8.7 | 80.4 | 9.8 | 38.4 | 5.4 |
| Population growth rate (%) | 0.1 | 0.42 | -0.17 | -0.26 | -0.16 | -0.02 |
|
Age Structure (%)
(15 to 64 years old)
|
65.37 | 66.55 | 64.81 | 65.84 | 67.73 | 68.84 |
|
Age Structure (%)
(65+ years old)
|
19.42 | 19.44 | 22.36 | 19.5 | 17.47 | 15.97 |
| Literacy (%) | 99.0 | 99.0 | 99.0 | 99.1 | 99.8 | 99.6 |
| Unemployment rate (%) | 2.9 | 5.5 | 3.8 | 4.2 | 4.9 | 8.1 |
| Inflation (%) | 2.4 | 2.2 | 1.7 | 2.4 | 2.0 | 1.3 |
| Population below poverty line (%) | 9.7 | 3.0 | 16.7 | 14.9 |
17.6
|
12.3 |
| GDP* (USD billions) | 375.9 | 441.0 | 4,199.0 | 289.6 | 1,126.0 | 179.7 |
| GDP real growth rate (%) | 4.3 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 4.0 | 4.7 | 3.4 |
| GDP per capita* (USD) | 35,500 | 50,000 | 50,800 | 29,600 | 29,600 | 33,100 |
| Public debt (% of GDP) | 34.7 | 78.6 | 63.9 | 73.6 | 50.6 | 50.9 |
| Industrial production growth rate (%) | 7.5 | 6.5 | 3.3 | 7.4 | 7.5 | 2.7 |
| Exports (USD billions) | 144.8 | 156.7 | 1,434.0 | 98.74 | 224.6 | 80.8 |
| Imports (USD billions) | 134.7 | 158.1 | 1,135.0 | 96.3 | 223.8 | 80.1 |
| Reserves of foreign exchange and gold (USD billions) | 148.0 | 21.57 | 200.1 | 28.0 | 113.3 | 3.6 |
| Currency | Koruna CZK |
Euro EUR |
Euro EUR |
Forint HUF |
Zloty PLN |
Euro EUR |
| Exchange rates (per USD) 09/11/2019 | 23.53 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 301.80 | 3.94 | 0.91 |
| Exchange rates (per EUR) 09/11/2019 | 25.90 | n/a | n/a | 332.29 | 4.34 | n/a |
| Rating in 2018 Corruption Perceptions Index** | 5.9 | 7.6 | 8.0 | 4.6 | 6.0 | 5.0 |
| Rating in 2019 Index of Economic Freedom*** | 73.7 | 72.0 | 73.5 | 65.0 | 67.8 | 65.0 |
* PPP ” Purchasing Power Parity
** 2018 Corruption Index: 10=Very Clean; 0=Highly Corrupt
*** 2019 Index of Economic Freedom: 100-80 = Free; 49.9-0 = Repressed
Economic Data from CIA World Factbook
2018 Corruption Perceptions Index, Transparency International
2019 Index of Economic Freedom, Heritage Foundation
Credit and Collections
Collecting in the Czech Republic
Statutes of limitations:
- Open Accounts: 4 years
- Promissory Note: 4 years
- Written Contracts: 4 years
- Oral Agreements: 4 years
Dispute Resolution
Commercial disputes, especially those related to bankruptcy, can drag on for years. New bankruptcy legislation came into effect July 1, 2007, and has accelerated the process somewhat.
The Czech Republic is a signatory of the 1958 Convention on the Recognition and Enforcement of Foreign Arbitral Awards, which came into effect in the Czech Republic in 1993.
Risk Assessment
Coface Country Rating: A3 — Changes in generally good but somewhat volatile political and economic environment can affect corporate payment behavior. A basically secure business environment can nonetheless give rise to occasional difficulties for companies. Corporate default probability is quite acceptable on average.
Coface Business Climate Rating: A2 — The political and economic situation is good. A basically stable and efficient business environment nonetheless leaves room for improvement. Corporate default probability is low on average.
Credendo Political Risk Rating: 1 — Lowest risk
Credendo Commercial Risk Rating: B — Moderate risk
The Belgian Export Credit Agency (ONDD): Risks on Export Transactions
- Political Risk – Short Term <2 years: 1 — lowest risk
- Political Risk – Medium-Long Term >2 years: 1 — lowest risk
- Commercial Risk: B — moderate risk
Other Risk Ratings
- Fitch: AA-
- Moody’s: A1
- S&P: A
Business Climate
Long term challenges facing the Czech Republic include a rapidly aging population, an unsustainable pension and health care system, and diversifying away from manufacturing and toward a more high-tech, services-based, knowledge economy.
Economic Freedom: The Czech Republic’s economic freedom score is 73.7 (2019 Index of Economic Freedom), making its economy the 23rd freest in the 2019 Index. The Czech Republic is ranked 13th out of 44 countries in the Europe region, and its overall score is higher than the regional and global averages.
Market Access: The Czech market is considered to be quite open and similar to other EU countries´ systems. The country joined the EU in May 2004 and the customs and other market access conditions are harmonized with those of the EU.
Regulatory System: Policy frameworks are consistent with a market economy. All laws and regulations are published before they enter into force and ppportunities for consultation on pending regulations exist. All interested parties, including foreign entities, can participate. However, bureaucracy and unnecessary red tape remain a source of complaints by both domestic and foreign investors.
Intellectual Property Rights: Existing legislation guarantees protection of all forms of property rights, both intellectual and physical.
Exchange Control: The Czech crown is fully convertible. Imports or exports equal to or exceeding 10,000 Euro (approximately CZK 259,000 or USD 11,000) in cash, travelers’ checks, money orders, securities or commodities of high value (such as precious metals or stones) must be declared at the border.
Expropriation: Government acquisition of property is done only for public works projects in a non-discriminatory manner. Any such act is one full compliance with international law.
Corruption: Allegations of corruption are common, especially in government procurement.
Political Violence: The risk of political violence in the Czech Republic is extremely low. There is no history of political violence or terrorism in modern times
For more detailed information on these topics, visit the 2019 Investment Climate Statement – Czech Republic, U.S. Department of State
Business Protocol in Czech Republic
- Business appointments are mandatory in the Czech Republic. Letters for initial appointments should be addressed to the company rather than a specific person. Friday afternoon is not a good day for appointments as after lunch many Czechs leave for their country homes (cottages) for extended weekends.
- Executives usually dress formally. Vivid colors are considered inappropriate. Women should wear conservative suits or dresses. Preferred colors for business are black, grey, brown, beige and dark blue.
- Crucial business decisions are often made outside the business environment as Czechs value hospitality as a means through which to build both personal and business relationships.
- Use of titles is extremely important in Czech business settings. Refer to your Czech counterparts as “Mr/Mrs.” “Dr”, or “Ing” (Engineer). Chairs and positions in the company are often more important than names.
- Presentations should be accurate, detailed and thorough. Have charts and figures to back up your claims.
More information on Business Protocol: Kwintessential
Sources for further information on doing business in the Czech Republic
American Chamber of Commerce in the Czech Republic
Doing Business in the Czech Republic – Baker McKensie
Embassy of the Czech Republic in Washington, DC
Embassy of the United States – Prague, Czech Republic
**********
Subscribe to the Credit-to-Cash Advisor
Monthly e-Newsletter — It’s Free
This information is provided by ABC-Amega Inc. Providing international receivable management and debt collection services for exporters to more than 200 countries including the Czech Republic. For further information, contact [email protected].
This report represents a compilation of information from a wide variety of reputable sources.
Comparative Economic Indicators: CIA World Factbook
Risk Assessment information: Coface Country Rating, Political Risk Insurance Center and Credendo.
Exchange Rates: OANDA.com The Currency Site.